Sustainability
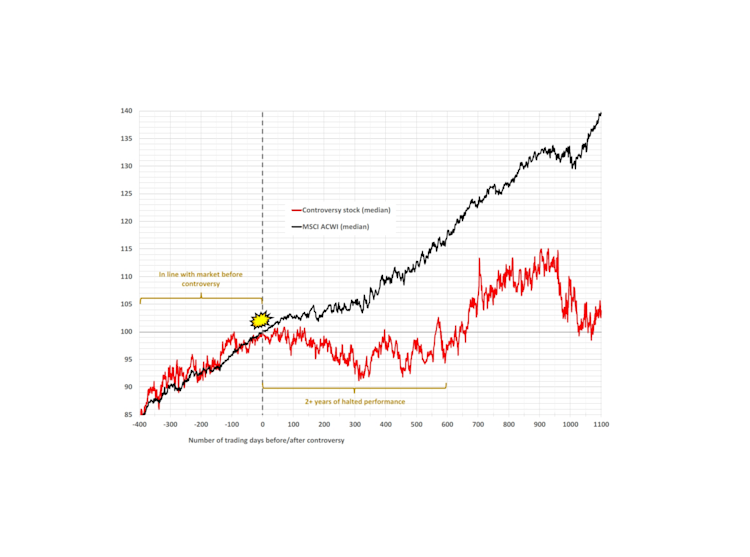
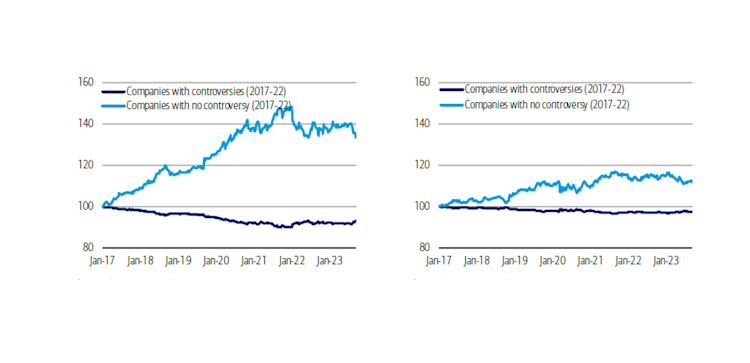
Costly controversies: the negative financial impact of ESG fallouts
Disclaimer
Degroof Petercam Asset Management SA/NV (DPAM) l rue Guimard 18, 1040 Brussels, Belgium l RPM/RPR Brussels l TVA BE 0886 223 276 l
Marketing Communication. Investing incurs risks.
The views and opinions contained herein are those of the individuals to whom they are attributed and may not necessarily represent views expressed or reflected in other DPAM communications, strategies or funds.
The provided information herein must be considered as having a general nature and does not, under any circumstances, intend to be tailored to your personal situation. Its content does not represent investment advice, nor does it constitute an offer, solicitation, recommendation or invitation to buy, sell, subscribe to or execute any other transaction with financial instruments. Neither does this document constitute independent or objective investment research or financial analysis or other form of general recommendation on transaction in financial instruments as referred to under Article 2, 2°, 5 of the law of 25 October 2016 relating to the access to the provision of investment services and the status and supervision of portfolio management companies and investment advisors. The information herein should thus not be considered as independent or objective investment research.
Past performances do not guarantee future results. All opinions and financial estimates are a reflection of the situation at issuance and are subject to amendments without notice. Changed market circumstance may render the opinions and statements incorrect.